
The porter’s five forces for John Lewis will be determined by the help of the different macro and the micro-economic issues faced by John Lewis. Each of the five forces depicted in the figure is described in detail below:
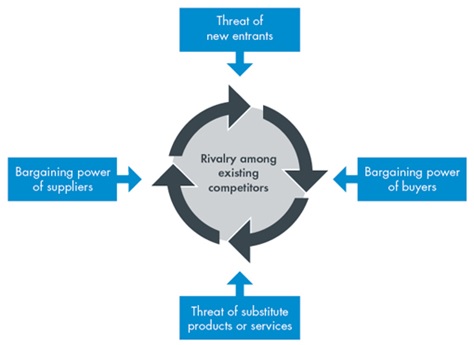
Threat of New Entrants
The threat of new department stores opening in London is relatively low as customer buying behaviour in UK is inclined towards respected and established stores. However UK’s food sector has witnessed many new entrants from time to tome such as Lidl and Aldi who are compete with John Lewis/Waitrose on price. Different companies who are not in this business are entering this market as a high potential market as a result threat grows on increasing every year. However In the department store business, the threat of new entrants is relatively low as the cost of capital is on a higher side for this segment. Also the department store is majorly driven by new product and innovation as new entrants in this sector always try to disrupt the market coming up with specialized products. Another primary reason behind the lower threat of new entrants is on account of investors not having full knowledge about the market.
Threat of Rivalry
The retail sector faces an intense competition with most of the leading companies are diversifying their business into new non-core sectors. John Lewis in its portfolio has a wide variety of products like household goods, clothing, drink and also food. Due to offering this wide range of products major competitors like Sainsbury, and Tesco are also diversifying into household goods and clothing. These companies draft their strategy as a single generic strategy, which could be either one of differentiation, low cost, or a combination of both which is driven by innovation and new product development. John Lewis even though had started with premium pricing strategy has had to cut down its prices as a result of tough competition from the market. The commitment of John Lewis to its customers though being one of the major point of difference for the company also leads to price reductions in line with other companies. The reduction of prices of its products however can lead to tampering of business image and product specialization as it leads to psychological barriers in minds of customers.
Bargaining power of suppliers
Bargaining power of their suppliers is relatively low which is quite the opposite compared to the bargaining power of customers. Owing to huge customer base John Lewis has an upper hand over suppliers as every supplier has a target to achieve the sales and achieve shelf space which can be catered via John Lewis. John Lewis which is UK’s one of the major retailer has high sales and good turnover over the years which makes it one of the first choices for suppliers to have their products on the shelves of the stores. Moreover John Lewis also has an integrated strategy of having retailing as well as having its own brands especially in sector like textiles where it purchases raw materials, and manufactures textiles, curtains and soft furnishings under its own brand name.
Bargaining power of buyers
John Lewis follows a philosophy which is driven by ‘never knowingly undersold’ strategy which guarantees customers of product quality and service. This makes customers have a hold on John Lewis ‘Offerings as well as pricing strategy. For instance we know that the products of John Lewis were priced at a premium price when it entered the market, however as competition grew and customers switched to low priced products John Lewis had to remodel its strategy and place it products at a lower price. Considering all these factors, if we analyse the bargaining power of John Lewis’ consumers, it looks comparatively high. As a result of high competition especially with sector like retail which faces price war on a regular basis, the switching cost is low. Moreover with Brexit the UK economy is expected to slow down which makes retailers subjected to lowering the prices further. Also, John Lewis is majorly dependent on UK market as the international presence is low; hence the bargaining power of John Lewis’ customers is high.
Threat of substitutes
The threat of substitutes in retail sector is not that high though there can be cases of high chance of substitutes with customers shifting to a discount store. For instance in times of shifts in the economy many stores especially like supermarkets, specialized stores and discount stores go for stock clearance which makes them offer substitutes for products purchased in department stores .In these situations consumers would be more inclined to purchase at a discount store than in a department store. Similarly, when there is a high disposable income and interest rates lower in the economy then customers would go for a premium product than a low priced product. So customers would prefer to go to stores like Harrods over John Lewis. To tackle such situations companies like John Lewis should adopt a flexible pricing strategy, Product specialization through private labels.
References

Mar 24, 2020

Sep 24, 2022